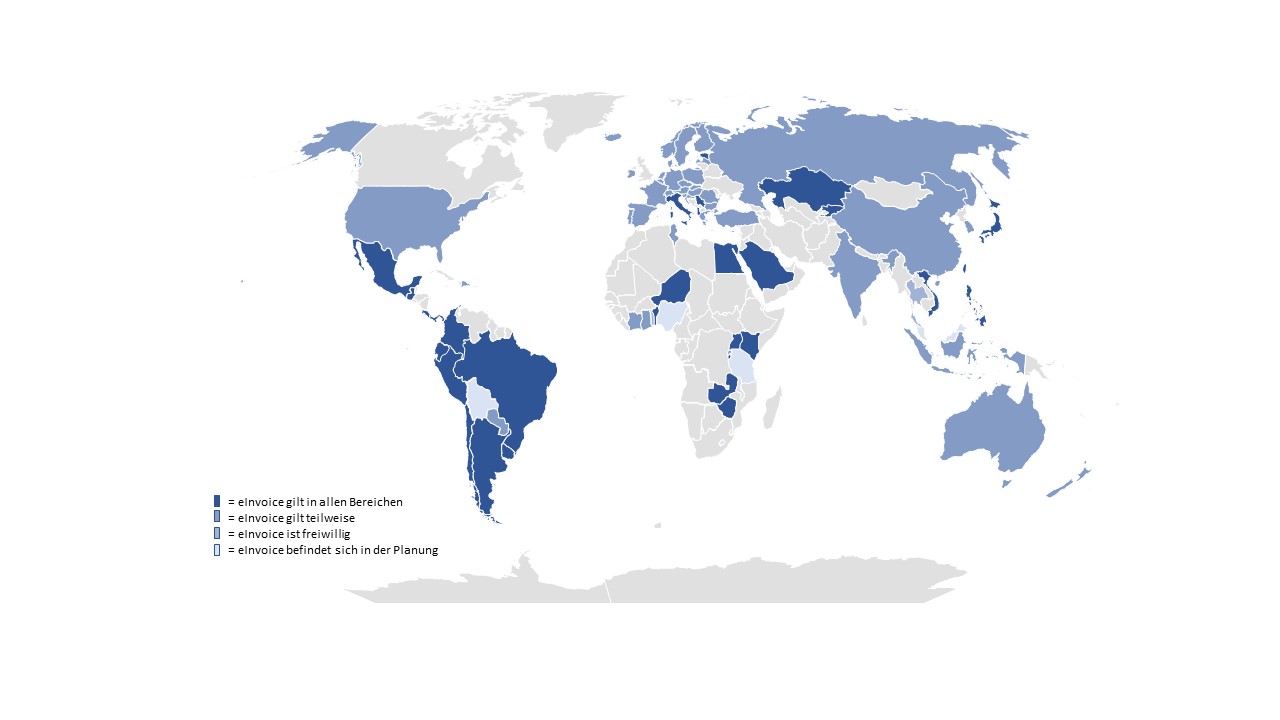
E-Invoicing regulations by country
Global e-invoicing obligations
In our overview you will find all countries that have already introduced or announced a B2G or B2B e-invoicing obligation.
We take care of the country format of your respective business partner and communication with the local tax authorities.
Egypt
Egypt is currently in the process of introducing e-billing by July 1, 2023. All companies selling taxable goods and services in Egypt are affected by the e-invoicing system.
Invoice formats:
A uniform format is not used. Invoices can be generated in Egypt in JSON or XML format.
You can already generate and send Egyptian e-invoices with our solution.
Andorra
The creation of e-invoices in the B2G area is mandatory for public clients. In the B2B area, the consent of the buyer is required.
Invoice formats:
Mandatory formats for invoicing are the UBL 2.1 or PEPPOL BIS format for B2B invoices. There are currently no specifications in the B2B area.
We can already generate and send e-invoices for Andorra with our solution.
Argentina
Since April 1, 2019, all companies in Argentina have been obliged to issue electronic invoices. These electronic invoices are based on an authorization code issued by the AFIP (Administración Federal de Ingresos Públicos). A certificate is required to sign this code, the so-called CAE (Código de Autorización Elecrónico). However, no electronic signature is required on the invoice, however the web service requesting the code must be signed with a digital certificate issued in Argentina.
Requirements: From March 1st, 2021, e-invoices must be provided with a QR code. The Electronic Authorization Code makes tax control easier as it is on the invoice which is then sent to the customer.
Invoice formats:
An XML format is required for the CAE, but the final invoice that the recipient receives can be in any standard format.
Albania
A new law was passed in Albania in 2021, setting new rules for e-invoicing.
Since then, more and more companies have been obliged to replace the traditional paper invoice with an electronic form.
This applies to
- B2G services: from January 1st, 2021
- B2B services (from July 1, 2021): companies that make deliveries to other companies
- B2C services (from September 1, 2021): companies that supply goods and services to customers who are not registered for tax purposes when payment is not made in cash
Invoice formats:
A uniform format is not used. Specifications for the basic use of e-invoice in Albania are UN/CEFACT (Interindustrial Invoice (Schema XML 16B)) and UBL 2.1 (ISO/IEC 19845:2015).
Australia
To date, only one obligation has been established for Commonwealth Agencies (public bodies working on behalf of the Australian Government). These had to introduce e-invoicing by July 1, 2022. It was also announced that all companies must connect to the Peppol network by July 2025.
Invoice formats:
The Peppol format PEPPOL BIS Billing 3.0. has established itself as the standard in Australia.
Bahrain
Bahrain plans to introduce its own e-invoicing system from 2024. What exactly this system should look like and who is obliged to use this system has not yet been determined.
Belgium
E-billing was introduced in Belgium in 2013. In the area of business-to-government (B2G) business relations, the use of e-invoices is now mandatory for both parties, ie for central and federal public administrations as well as for their suppliers. In the private sector, on the other hand, the use of e-bills is voluntary and dependent on the acceptance of the recipient. From July 2024, e-invoicing will be mandatory in the B2B sector.
Invoice formats:
Also in Belgium the format is PEPPOL BIS 3.0 now become the standard.
benin
In 2020, the e-invoice was introduced in Benin under the name Facture normalisée.
This obligation applies to all VAT registered companies. The tax authority Direction Générale des Impots (DGI) assigns each registered invoice its own QR code.
Invoice formats:
The JSON format is used as the invoice format.
Bolivia
The Virtual Invoicing System is currently being actively introduced in Bolivia. There is no obligation to date. Issued invoices must show a Unique Daily Invoicing Code – CUFD assigned by the Servicio de Impuestos Nationales (SIN). The e-invoicing obligation will be introduced step by step. From April 1st, 2023, selected taxpayers should start issuing e-invoices.
Invoice formats:
There is currently no uniform format. The only requirement is the representation in the usual XML format.
Brazil
In Brazil, it is mandatory for all taxpayers to issue e-invoices in various formats called Fiscal Notes, all in XML.
Invoice formats:
Depending on the type of object to be invoiced, there are different structures for these invoices, such as NF-e for products, NFS-e for services or CT-e for the transport of goods.
Bulgaria
With the introduction of the eFaktura.bg system in 2007, which is now used by more than 500 invoice issuers from various industries, the process of electronic issuing, transmission, receipt and processing of invoices has been automated.
Invoice formats:
There is no standard format required.
burundi
Since 2022, a real-time electronic return to the OBR (Office Burundais des Recettes) of invoices is mandatory for all VAT-registered and foreign companies with a local tax representative.
Invoice formats:
There is no uniform specification of the invoice format.
Chile
In 2003, Chile was a pioneer country in the development of an e-invoicing system and thus also provided other Latin American countries such as Brazil and Mexico with the basis for their own systems, which have now become established. Despite its pioneering role, Chile only began the widespread introduction of electronic invoices in 2014 and completed it in February 2018 with the implementation of the system in rural micro-enterprises. There is a 100% obligation for sender and recipient.
Invoice formats:
In Chile, the country-specific e-invoice format DTE (a local XML format) unified and standardized.
China
China is currently reforming its current invoicing system, initially only making e-invoicing mandatory for new taxpayers in the B2G and B2C sectors, but making it optional for everyone else. The new E-Fapiao e-invoicing system is a modernization of the existing Golden Tax System (GTS), which also includes the submission of paper VAT invoices. By 2025, the creation and receipt should be mandatory for everyone.
Invoice formats:
There is no uniform e-invoice format in China. The only requirement is, as usual, an XML-based representation.
Costa Rica
The Costa Rican government started its e-invoice project in 2017 with a phased rollout that ended in 2018. Since then, the use of e-invoices has been mandatory for all taxpayers, both for issuing and receiving.
Invoice formats:
There are several XML-based digital documents in Costa Rica: e-invoice, e-sales receipt, e-export invoice, credit note and debit note.
Denmark
Since 2005, in the B2G area, both the Danish authorities and their suppliers have been obliged to send e-invoices in the national format via the NemHandel network. The Danish parliament passed a new accounting law in May 2022, which obliges companies to exchange and archive invoices electronically. Implementation in the B2B area started in 2022. Depending on the size of the company, the obligation will take effect at a different time. Sending e-invoices will be mandatory by July 1st, 2026.
The new Danish Accounting Act brings many innovations, the most important of which is the requirement to issue, exchange, receive, process and archive invoices electronically. At the same time, software providers of corresponding services must be registered with the Danish Economic Authority ERST (Danish: Erhvervsstyrelsen) and receive the status of a "digital accounting system".
Invoice formats:
In Denmark, the national UBL 2.0 standard OIOUBL is mandatory. The use of Peppol BIS 3.0 UBL is voluntary.
Germany
Electronic invoicing in the public sector (B2G) in Germany is mandatory due to European regulations and each federal state has set its own guidelines for invoicing. Electronic invoices are currently only mandatory for public administrations and suppliers of the federal government, the federal state of Baden-Württemberg, Bremen, Hamburg, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and Saarland. Rhineland-Palatinate and Hesse will follow in 2024.
In the B2B sector, companies have been able to issue electronic invoices on a voluntary basis since 2011, as long as the recipient agrees. The ability to receive and process electronic invoices is required for all federal contracting authorities. In addition, all federal states must enact their own laws on electronic invoicing.
More information on the plans of the federal states to make e-billing mandatory can be found here.
Invoice formats:
In Germany, the e-invoice formats XRechnung, PEPPOL BIS and ZUGFeRD 2.1 have become established.
Dominican Republic
The use of e-bills has been voluntary since 2019. The e-invoicing obligation is currently being gradually implemented in the Dominican Republic in the B2B area in three steps:
– Large companies (2023)
– Large local and medium-sized companies (2024)
– Small companies (from 2025)
The procedure is implemented by the Dirección General de Impuestos Internos (DGII).
Invoice formats:
Invoices can be generated in the Dominican Republic in XML format based on the UBL standard.
Ecuador
From November 30, 2022, the creation of electronic invoices will be mandatory for taxpayers. In 2014, certain companies and public bodies were already obliged to issue e-invoices by the SRI (Servicio de Rentas Internas).
Invoice formats:
Invoices must be issued in local XML format.
Ivory Coast
In 2019, Côte d'Ivoire introduced an e-invoicing obligation, under which only technology companies offering digital goods or services in the B2B and B2C sectors are obliged to do so.
Invoice formats:
A uniform format is currently not planned.
ElSalvador
In El Salvador, e-invoicing is currently being introduced gradually. There is currently no concrete plan. So far, issuing electronic invoices has been voluntary.
Invoice formats:
A local JSON format is planned.
Estonia
The use of electronic invoices in the B2G area in Estonia is mandatory for public administrations and suppliers. Since 2017, all public bodies are required to receive and process e-invoices, while suppliers are required to issue e-invoices since 2019.
Invoice formats:
Invoices can be created in Estonia in the national XML format (EVS 923:2014/AC:2017), the European standard UBL 2.1 and the UN/CEFACT CII. A PDF is sufficient from foreign providers.
Finland
Electronic invoicing is widespread in both public administrations and private companies. In the B2G sector, since 2010 all public administrations have preferred to receive invoices in electronic form, although there was no obligation until 2020 due to European public procurement legislation. While it is not mandatory in the private sector, it is very widely used by companies (due to the great benefits the system offers).
As part of the implementation of Directive 2014/55/EU, public institutions must be able to receive electronic invoices from 2020. However, the transmission to the suppliers is only necessary if an authority bills more than EUR 10,000 per year.
Invoice formats:
Finvoice is Finland's national e-invoicing format and is used by many companies and public institutions. TEAPPSXML (Technical Approval for Public Sector e-Invoicing), which is based on the international e-invoicing standard UN/CEFACT Cross-Industry Invoice (CII), has been specially adapted for use in the Finnish public sector.
France
Since 2020, there has been a B2G obligation for the creation of e-invoices in France. A B2B obligation is to be introduced between July 2024 and January 2026. The introduction will take place in three phases. From July 2024, large taxpayers will be obliged to issue e-invoices. Mid-range taxpayers as of January 2025 and all other taxpayers as of January 2026.
Invoice formats:
The e-invoices can be in the formats UBL 2.0, UBL 2.1, CII 16B, CPP, PES; PDF; PEPPOL BIS and Factur-X are issued.
Ghana
Since October 1st, 2022, Ghana has started to introduce e-invoicing to the country's 600 largest companies. From 2024, all companies are to be converted and issue certified e-VAT invoices.
Invoice formats:
A specific invoice format is not required in Ghana.
Greece
Greece adheres to the European Directive 2014/55/EU and has made the receipt and processing of e-invoices obligatory for public clients in the B2G sector.
Invoice formats:
The invoice format used only has to be EN-compatible.
Great Britain
From April 2022, the principle of MTD (Making Tax Digital) will be mandatory for all companies and provides for invoices to be created electronically. However, companies could also apply the principle voluntarily in advance.
Invoice formats:
So far, no uniform invoice format has been provided for e-invoices.
Guatemala
Since September 2019, all taxpayers who provide general individual services are obliged to comply with the FEL (Factura electrónica en línea) e-invoicing model. The introduction will be carried out in stages. From April 1st, 2023, all taxpayers are obliged to only create, send and receive electronic documents.
Invoice formats:
Currently, all that is required is the creation of a structured XML file.
Hong Kong
There is currently no obligation in Hong Kong. Public clients in the B2G sector are obliged to receive e-invoices.
Invoice formats:
Electronic invoices can be created in PDF, doc, docx, xls and xlsx formats.
India
In 2019 it was decided to phase in the e-invoicing obligation in India. The introduction is currently being implemented in phase five. From January 01, 2023, all taxpayers with income over 5 croses INR (approx. €624,000) are required to use e-invoicing. There are currently no obligations to receive e-bills, and there is also no planned phased rollout.
Invoice formats:
E-invoices must be created in JSON format according to the GST INV-1 scheme. The GST INV-1 scheme is based on the PEPPOL/UBL.
Indonesia
From July 1st, 2015, taxpayers in Java and Bali are obliged to use e-invoices. Since July 1st, 2016, this has been mandatory in all other regions of Indonesia.
Invoice formats:
There is currently no uniform formatting requirement for Indonesia.
Ireland
In Ireland there is a B2G regulation for e-invoices. Mandatory for public administration and voluntary for public suppliers. In the B2B area there is no obligation yet. Buyers can consent to receiving e-invoices.
Invoice formats:
The format used nationally is PEPPOL BIS. The local public administrations have defined their own CIUS-CEFACT.
Iceland
Iceland is aligning itself with the applicable EU Directive 2014/55/EU when introducing e-invoicing. Therefore, there is only an obligation in the B2G area for public administrations and their suppliers. In the B2B area, the buyer's consent is required to receive e-invoices.
Invoice formats:
In Iceland, the formats UBL 2.1 and PEPPOL BIS are mandatory.
Israel
The Israeli authorities plan to introduce mandatory e-invoicing based on the Chilean model. It is not yet known when that will happen.
Invoice formats:
There is no precise information on this yet.
Italy
In Italy B2G invoices have been mandatory since 2014 and since 2019 this also applies to private companies (B2B). In the B2B sector, Italy was the first country in Europe to introduce nationwide e-invoicing. The obligation applies to the creation, sending and receipt of e-bills.
Invoice formats:
Nationwide, the FatturaPA (XML) format is mandatory for all e-invoices created and must comply with the Exchange System (SDI).. The PEPPOL BIS format is intended for orders.
You can find more information about e-invoicing in Italy here.
Japan
From October 2023, the creation of e-invoices will be mandatory in Japan. It must be possible to exchange invoices electronically via the PEPPOL network.
Invoice formats:
It is intended to use the PEPPOL format for exchanging e-invoices.
Kazakhstan
The introduction of e-billing began in Kazakhstan in 2016. E-billing has been mandatory for all companies since 2019. A central portal is responsible for validating the invoices, assigning invoice numbers, delivery and archiving.
Invoice formats:
The invoices must be created in an XML format.
Kenya
Since September 30, 2022, all VAT payers must comply with the obligation to create an e-invoice. The whole thing is implemented via the Tax Invoice Management System (TIMS).
Invoice formats:
In Kenya, the JSON format is mandatory for the creation of e-invoices.
Kyrgyzstan
Since January 1st, 2023, all persons and companies involved in the economy have been obliged to issue e-invoices. Invoices are to be exchanged, received and created via the system provided by the tax authority ETTN.
Invoice formats:
There are currently no exact formatting requirements.
Colombia
Since 2019 in Colombia it is mandatory for all companies to issue electronic invoices with prior validation.
Invoice formats:
The standard invoice format is XML, version UBL V2.1 CO.
Croatia
Since 2019, there has been a B2G obligation for the creation of e-invoices in Croatia. There is currently no obligation in the B2B sector.
Invoice formats:
In Croatia one of the formats PEPPOL BIS, UBL 2.1 or CII is mandatory.
Lesotho
In Lesotho, the government is currently planning mandatory e-invoicing for B2B, B2C and B2G. When and how the implementation will look like is currently not known (as of March 2023)
Latvia
E-invoices are currently mandatory in Latvia in the B2G area for public administrations and voluntary for public suppliers. From 2025, e-billing will be mandatory in the B2G and B2B areas.
Invoice formats:
The PEPPOL BIS 3.0 format is mandatory nationwide.
Lichtenstein
In Lichtenstein, receiving e-invoices is mandatory for central and sub-central/local authorities. For all other areas there are currently no obligations for the creation of e-invoices.
Invoice formats:
The e-invoices can be created in XML or PDF format.
Lithuania
Since July 2017, electronic invoicing has been mandatory in Lithuania in the B2G sector. In the private sector, e-billing is currently voluntary. A commitment is not yet planned here.
Invoice formats:
Here the format PEPPOL BIS 3.0 – national XML format is prescribed.
Luxembourg
Since April 2019, public clients in Luxembourg have been obliged to receive and process invoices electronically. In May 2022, the gradual introduction of the obligation to send e-invoices began. From March 18, 2023, all companies will be obliged to send e-invoices to public institutions.
Invoice formats:
The PEPPOL BIS 3.0 format is mandatory nationwide for e-invoices created.
Malaysia
From August 2024, Malaysia will make electronic invoicing mandatory.
Invoice formats
The following formats will be available for the transmission of electronic invoices: XML and JSON
You can find more information about e-invoicing in Malaysia here.
Malta
Malta joins compliance with European Directive 2014/55/EU by requiring all public administrations to receive e-invoices.
Invoice format:
So far, the PEPPOL format is planned. A separate country-specific format is currently being developed.
Mauritius
A gradual rollout for the introduction of e-invoicing is currently being planned. There is currently no exact timetable.
Invoice format:
All that is currently known is that invoices have to be sent to the tax authorities and that they have to be provided with a QR code.
Mexico
An e-invoicing system was introduced in Mexico in 2004 and is being continuously improved. There is an e-invoice obligation in the B2B, B2C and B2G areas when creating, sending and receiving.
Invoice formats:
The digital tax document Comprobante Fiscal Digital por Internet 4.0 (CFDI 4.0) is a structured XML file that is submitted to the tax authority SAT. This format specification applies from April 2023.
New Zealand
In 2018, the New Zealand government launched the "Australia and New Zealand Government Electronic Invoicing Arrangement" together with Australia. Only a few authorities in the B2G sector are currently obliged to receive e-invoices.
Invoice formats:
In New Zealand, the PEPPOL BIS Billing 3.0 format is mandatory.
Netherlands
The use of electronic invoices is mandatory for public administrations and voluntary in the B2B sector.
Invoice formats:
In the Netherlands the formats SI-UBL 2.0, PEPPOL BIS 3.0 and NL CIUS are mandatory.
Niger
Since 2021, Niger has made e-invoicing compulsory for all VAT-registered companies.
Invoice formats:
There is no prescribed format in Niger.
Nigeria
A requirement to submit e-invoices for imports and exports was announced by the Nigerian government in 2022. Excluded are invoices under 10,000 $. If a supplier's annual invoice value is more than 500,000 $, invoices must be submitted electronically.
Invoice formats:
Exact information is not yet available.
Norway
In Norway, receiving and managing e-invoices in the B2G sector has been mandatory for all public administrations since 2019. From 2023, this obligation will also apply to the sending of e-invoices by suppliers in the B2G sector. There is currently no obligation for the B2B sector.
Invoice formats:
E-invoices can be issued in Norway in PEPPOL BIS 3.0 format or in the national EHF Billing 3.0.
Austria
In Austria there is a B2G obligation for the creation and sending of e-invoices. To date, there is no obligation in the B2B sector.
Invoice formats:
Nationwide, the invoices can be issued in the national ebInterface format, UBL format or in the PEPPOL BIS format.
Panama
Panama is currently in the process of introducing an e-invoicing system. Since July 2022, there has been a B2G obligation for the creation of e-invoices. From June 30, 2023, a nationwide B2B obligation will apply.
Invoice formats:
A digitally signed XML file is mandatory in Panama.
Paraguay
In 2017, the country of Paraguay started adopting e-invoicing. Since 2019, in addition to the companies already required by the government, all other companies can voluntarily register in the national SIFEN system. From October 2024, the creation of e-invoices will be mandatory for all areas. Companies registered after January 1st, 2024 are already obliged to create, send and receive electronic invoices.
Invoice formats:
The standard XML file is provided here for creating the e-bill.
Peru
In 2014, the gradual introduction of the e-invoicing obligation in Peru began. Since 2021, 100% all taxpayers are required to issue, receive and send e-invoices.
Invoice formats:
A standardized XML format is planned nationwide, which uses the adapted version UBL V2.1.
Philippines
Since July 1st, 2022, e-invoicing has been mandatory for the 100 largest companies in the country. In January 2023, the introduction of the EIS (Electronic Invoicing System) for all companies based in the country began.
Invoice formats:
The generated e-invoices must be created in JSON format.
Poland
Since 2019, Poland has had an e-invoicing obligation in the B2G area for public administrations. In the B2B sector, it will be mandatory for dispatch, receipt and issuance in 2024. Initially, an obligation from January 2024 was planned, but this has been postponed to July 2024.
Invoice formats:
The formats UBL 2.1, UN/CEFACT CII or PEPPOL BIS 3.0 are intended for the creation of e-invoices in Poland. From July 2024, only the FA_VAT format, a structured XML file, may be used.
Portugal
Public administrations are obliged to receive e-invoices. There has been a phased adjustment plan for suppliers in the B2G area since January 2021. For B2B it remains voluntary for the time being.
Invoice formats:
The formats UBL 2.1 "CIUS-PT" and CEFACT "CIUS-PT" are planned nationwide. Until December 31, 2023, e-invoices may also be generated as PDFs.
Rwanda
Since 2022, invoices in Rwanda can only be generated via the government invoicing system.
Russia
Since July 2021, only e-invoices for imported, traceable goods have been mandatory in Russia. There is no obligation in the other areas.
Invoice formats:
An RU-XML format is required as a mandatory format.
Romania
Since July 1, 2022, e-invoicing has been mandatory in the B2G area for public administrations and in the B2B area for products with a high tax risk. From 2024 there should also be an obligation in the B2B area, but it is unlikely that the schedule will be met at this point in time (as of March 2023).
Invoice formats:
In Romania, UBL 2.1 is intended as the uniform format.
Zambia
In Zambia, the creation of e-invoices in both B2B and B2C areas is mandatory.
San Marino
Since July 01, 2022, e-invoicing is mandatory for suppliers of goods and services between Italy and San Marino.
So far there are no further obligations for electronic invoicing.
Invoice formats:
Only a structured XML file is provided for e-invoices between Italy and San Marino.
Saudi Arabia
In Saudi Arabia, the e-invoicing obligation in the B2B, B2C and B2G areas will be introduced in two phases. The first phase started in December 2021. The second phase of the rollout starts on July 01, 2023.
Invoice formats:
In the first phase of the introduction of e-invoicing, the e-invoices must be created in any structured XML format. With the beginning of the second phase of implementation, the formats UBL 2.1. KSA or hybrid provided.
You can find more information about invoicing in Saudi Arabia here.
Sweden
Electronic invoicing has been mandatory in the public sector in Sweden since 2019. The use is voluntary in the private sector.
Invoice formats:
In Sweden, the invoice formats PEPPOL BIS 3.0, Svefaktura or SFTI ESAP 6 Fulltextfaktura are intended for created e-invoices.
Switzerland
In Switzerland, EInvoicing is only mandatory for public administrations and their suppliers. For the suppliers, however, only if the value of the invoice exceeds CHF 5,000 (approx. €4,594.57).
Invoice formats:
swissDIGIN-Yellowbill 2.0 or EDIFACT ABADOC are the mandatory billing formats for Switzerland.
Serbia
Electronic invoicing was gradually introduced in Serbia. In May 2022, reception and storage became mandatory for public administrations. From July 2022, e-invoices had to be sent from public administrations to companies and they had to be able to receive and save the e-invoices. Since January 2023, the obligation has also applied in the B2B sector.
Invoice formats:
UBL 2.1 is intended as the invoice format.
Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe has followed the example of some other African countries and since January 2022 has made it mandatory to submit electronic invoices via an electronic tax register. Information about taxpayers' transactions is transmitted in real time to the tax authority ZIMRA.
Slovakia
From April 2023, e-billing will be mandatory for B2G transactions. There will also be an obligation in the B2B area.
Invoice formats:
There is no specific invoice format for e-invoices.
Slovenia
E-invoicing has been mandatory in Slovenia in the B2G sector since 2015. A commitment in the B2B area is also being sought.
Invoice formats:
Electronic invoices can be sent in the national e-Slog 2.0 format, PEPPOL BIS 3.0 format or in UBL 2.1 format
Spain
Electronic invoicing has been mandatory in the B2G sector for several years. Since 2018, an e-invoice between subcontractors and contractors has been mandatory for amounts over €5,000. In the B2B sector, e-invoicing will be introduced gradually between 2024 and 2025. First for companies with an annual turnover of more than 8 million euros.
Invoice formats:
A structured XML document is provided, which is in the FACTURAE format.
South Korea
E-invoicing was introduced in South Korea in 2011 in the B2B and B2G areas and is being continuously expanded. In 2014, companies with annual sales exceeding KRW 300 million were required to issue e-invoices. From July 1, 2022, companies with sales of KRW 200 million or more and from July 01, 2023 with sales of KRW 100 million or more (approx. 73,000 euros).
Invoice formats:
A structured XML file is provided as the invoice format here.
Taiwan
Since 2021, e-invoicing, also known as eGui, has been mandatory for every Taiwan-based company.
Invoice formats:
For the generated e-invoices, the XML-based MIG-3.2.1. provided and must comply with government regulations.
Tanzania
The gradual introduction of e-billing in Tanzania is currently being promoted. For this purpose, the VFD (Virtual Fiscal Device) will be expanded.
Invoice formats:
E-invoices must be provided with a verification code and a QR code, which is assigned by the tax authority (TRA).
Thailand
Invoice formats:
The e-invoice is in the ETDA standard format (XML format). The end user receives his invoice as a PDF/A3 file.
Togo
Invoice formats:
In Togo, no invoice format is specified for the creation of e-invoices.
Czech Republic
Invoice formats:
The envisaged mandatory format is EN-compatible according to the law. In practice, the local ISDOC is used.
Tunisia
Invoice formats:
Türkiye
Invoice formats:
E-invoices must be created in the UBL-TR 1.2 TEMEL/TICARET E-FACTURA format. Export invoices are to be created in UBL-TR1.2 format
Uganda
Since January 1st, 2022 there has been an e-invoicing obligation and an e-ticket obligation in the B2B / B2C as well as in the B2G area.
Invoice formats:
The JSON format is intended here as an e-invoice format.
Further information on the e-invoicing requirement in Uganda can be found here.
Hungary
Invoice formats:
E-invoices can be created in UBL 2.1, UN/CEFACT CII or PEPPOL BIS 3.0 formats or as an electronically signed PDF.
Uruguay
Invoice formats:
In Uruguay, a structured document in XML format is provided with a syntax defined and maintained by the DGI (Dirección General Impositiva). This document is called the CFE (Electronic Tax Receipt).
USA
Invoice formats:
The OASIS UBL 2.X format for invoice and credit note documents is intended as the invoice format in the USA. The structured file can contain attachments and an electronic signature must be noted on it.
Vietnam
Invoice formats:
Only an XML format is provided here as the invoice format.
Cyprus
Invoice formats:
CIUS or PEPPOL BIS 3.0 are intended as invoice formats.


